However, if a state law requires a par (or stated) value, the accountant is required to record the par (or stated) value of the common stock in the account Common Stock. On the flip side, proven and mature stocks should have far more retained earnings than paid-in capital. The significance of this measure lies in its ability to provide a snapshot of investor commitment beyond the nominal share value, offering a historical perspective on shareholder equity contributions. As such, it serves as an important indicator for analysts assessing a company’s capital structure and financing strategy. Understand the nuances of paid in capital over par value and its implications for financial reporting and equity valuation in corporate finance.
Is Paid in capital in excess of par on a balance sheet?

Paid-in capital is the amount that the corporation has received from stockholders when issuing its stock. Retained earnings are the total amount of net income earned by a corporation (after tax) since its inception. This figure also leaves out the dividends that have been paid to stockholders since the business started. First, paid-in capital and retained earnings are the major categories of stockholders’ equity. HoneySlam can also credit common stock or paid-in capital for $200,000, and the additional $1.7 million will be credited as additional paid-in capital.
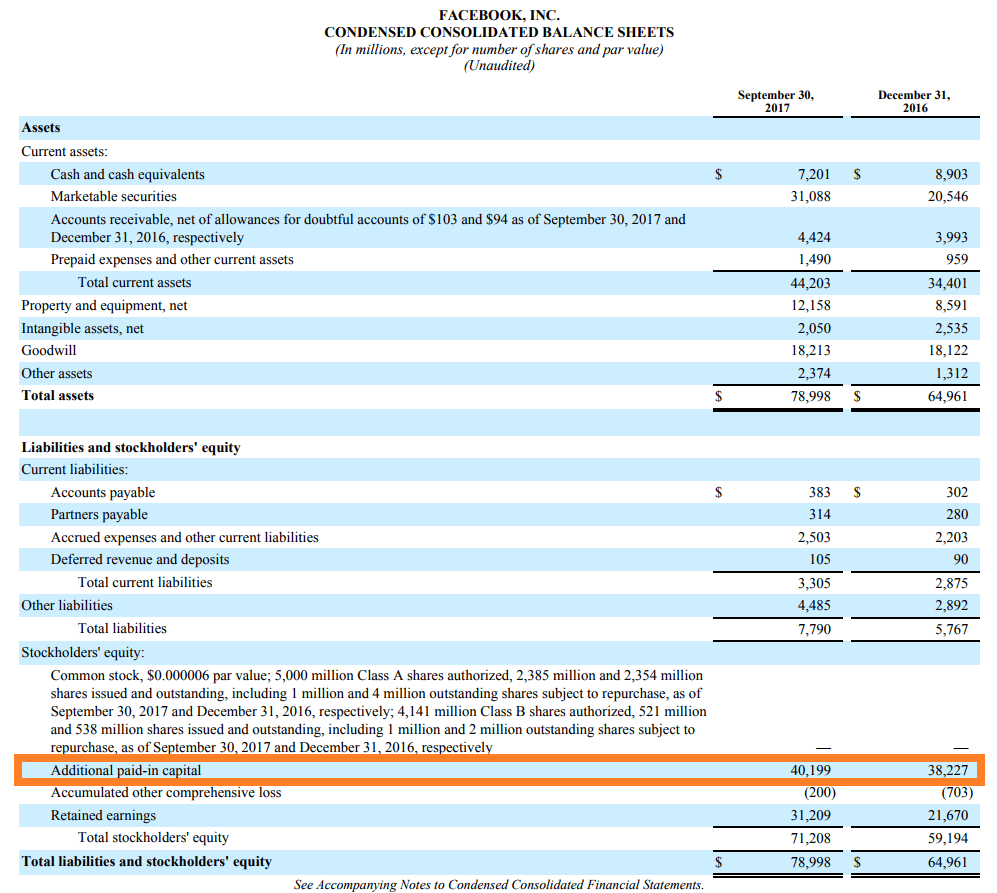
Shareholders’ equity for McDonald’s
Additional paid-in capital is shown in the Shareholders’ Equity section of the balance sheet. A company might be allocating capital to current assets, meaning they need short-term cash. Or the company could be expanding its market share by investing in long-term fixed assets. It’s also important to know how the company plans to raise the capital for their projects, whether the money comes from a new issuance of equity, or financing from banks or private equity firms.
- Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology.
- Therefore, the company’s balance sheet itemizes $1 million as “paid-in-capital,” and $10 million as “additional paid-in capital”.
- And additional paid-in capital is also known as capital in excess of par value or capital surplus.
- If not distinguished as its own line item, there will be a debit to cash for the total amount received and credits to common or preferred stock and additional paid-in capital.
FAR CPA Practice Questions: Issuing Stock, Stock Dividends, and Stock Splits
Par value is a nominal value assigned to a security by the issuing company, which is often set at a minimal amount, such as $0.01 or $1.00 per share. This figure is largely symbolic but serves a legal purpose in some jurisdictions, representing the minimum price for which a share can be sold upon initial offering. The par value is determined by the company at the time of incorporation and is typically recorded in the company’s articles of incorporation. It remains unchanged regardless of the actual market value of the stock, which can fluctuate significantly based on investor demand and market conditions. So Orange Guitars, Inc. would debit cash for the $1,000 and credit common stock for the $1 par value of $100 and credit paid in capital in excess of par for $900. Paid in capital in excess of par is essentially the difference between the fair market value paid for the stock and the stock’s par value.
The total cash generated from APIC is classified as a debit to the asset section of the balance sheet, with the corresponding credits for APIC and regular paid in capital located in the equity section. The interplay between these two accounts is a reflection of the company’s fundraising efforts and investor paid in capital in excess of par sentiment. These activities can bolster a company’s equity without diluting existing shareholders’ value, as they represent additional funds coming into the business. Excess received from shareholders over the par value (or stated value) of the stock issued; also called contributed capital in excess of par.
The figure for paid-in capital will include the par value of the shares plus amounts paid in excess of par value. HoneySlam, Inc. wants to put common stock in the amount of 100,000 shares on the market at a par value of $2. Before retained earnings start building up, a large part of a company’s equity usually comes from APIC. The primary market is the part of the capital market that issues new securities. It is through the primary market that people invest in a corporation by purchasing stock, raising the corporation’s PIC figure.
Of that $5,000, $4 would be considered paid-in capital in excess of par common stock, because the shares were sold for $1 above the par value of $1 per share. Understanding the nuances of financial statements is crucial for finance professionals, as these documents hold key insights into a company’s fiscal health. Among the various components that make up these statements, paid in capital in excess of par value often emerges as a critical figure. This metric not only reflects the initial funding dynamics but also carries implications for both the company and its investors over time. If not distinguished as its own line item, there will be a debit to cash for the total amount received and credits to common or preferred stock and additional paid-in capital.
Multiplying $45 by the total number of shares (20,000) gives us a total APIC of $900,000. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Paid-in capital may not be a headline number for a company, but it’s worth taking note of it as an investor.
